Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market Growth, Size, Trends, Share, Revenue and Future Outlook
Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market Size- By Technology, By Waste Type, By Application- Regional Outlook, Competitive Strategies and Segment Forecast to 2033
| Published: Sep-2024 | Report ID: POAE2481 | Pages: 1 - 108 | Formats*: |
| Category : Power & Energy | |||
- The Thang Long-Bac Ninh WtE facility in Bac Ninh province was officially opened in March 2024, with Finnish parliament speaker Jussi Halla-aho present. The facility, supplied by Valmet of Finland, is valued about VND 1.4 trillion (roughly USD 56.5 million). It uses cutting-edge circular technology to process 500 tons of waste per day and generate 11 MW of electricity.
- A waste-to-energy (WtE) plant in Phu Lang village, Bac Ninh province, was opened in November 2023. The plant treats industrial and household garbage to generate electricity. The Republic of Korea's Chosun Refractories ENG Co., Ltd. and Vietnam's Green Star Environmental Company Limited. together invested in this innovative facility, which can treat 800 tons of garbage each day.

| Report Metric | Details |
| Market size available for years | 2020-2033 |
| Base year considered | 2023 |
| Forecast period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments covered | By Technology, By Waste Type, By Application |
| Regions covered | Eastern region, Western region, Southern region, Northern region |
| Companies Covered | Vietnam Waste Solutions (VWS), Tam Sinh Nghia Investment and Development JSC, Hitachi Zosen Corporation, Watrec Ltd, Becamex IDC Corp., Hau Giang Biomass Power Joint Stock Company, Vietstar Joint Stock Company, T&J Green Energy, Thuan Thanh Environment Joint Stock Company (TT), and C&G Environmental Protection Holdings Ltd. |
- Government Authorities
- Waste Management Companies
- Energy Providers
- Investors
- Academic and Research Institutions
| By Technology: |
|
| By Waste Type: |
|
| By Application: |
|
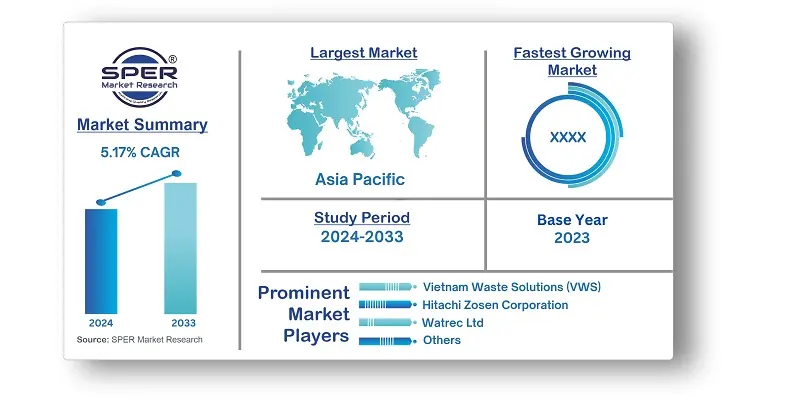
- Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market Size (FY’2024-FY’2033)
- Overview of Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market
- Segmentation of Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market By Technology (Thermochemical, Biochemical, Others)
- Segmentation of Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market By Waste Type (Municipal Solid Waste, Process Waste, Agriculture Waste, Others)
- Segmentation of Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market By Application (Electricity, Heat)
- Expansion Analysis of Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market
- Problems and Obstacles in Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market
- Competitive Landscape in the Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market
- Impact of COVID-19 and Demonetization on Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market
- Details on Current Investment in Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market
- Competitive Analysis of Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market
- Prominent Players in the Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market
- SWOT Analysis of Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market
- Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market Future Outlook and Projections (FY’2024-FY’2033)
- Recommendations from Analyst
1.1. Scope of the report1.2. Market segment analysis
2.1. Research data source2.1.1. Secondary Data2.1.2. Primary Data2.1.3. SPER’s internal database2.1.4. Premium insight from KOL’s2.2. Market size estimation2.2.1. Top-down and Bottom-up approach2.3. Data triangulation
4.1. Driver, Restraint, Opportunity and Challenges analysis4.1.1. Drivers4.1.2. Restraints4.1.3. Opportunities4.1.4. Challenges4.2. COVID-19 Impacts of the Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market
5.1. SWOT Analysis5.1.1. Strengths5.1.2. Weaknesses5.1.3. Opportunities5.1.4. Threats5.2. PESTEL Analysis5.2.1. Political Landscape5.2.2. Economic Landscape5.2.3. Social Landscape5.2.4. Technological Landscape5.2.5. Environmental Landscape5.2.6. Legal Landscape5.3. PORTER’s Five Forces5.3.1. Bargaining power of suppliers5.3.2. Bargaining power of buyers5.3.3. Threat of Substitute5.3.4. Threat of new entrant5.3.5. Competitive rivalry5.4. Heat Map Analysis
6.1. Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market Manufacturing Base Distribution, Sales Area, Product Type6.2. Mergers & Acquisitions, Partnerships, Product Launch, and Collaboration in Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market
7.1. Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market Size, Share and Forecast, By Technology, 2020-20267.2. Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market Size, Share and Forecast, By Technology, 2027-20337.3. Thermochemical7.3.1. Incineration7.3.2. Pyrolysis7.3.3. Gasification7.4. Biochemical7.5. Others
8.1. Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market Size, Share and Forecast, By Waste Type, 2020-20268.2. Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market Size, Share and Forecast, By Waste Type, 2027-20338.3. Municipal Solid Waste8.4. Process Waste8.5. Agriculture Waste8.6. Others
9.1. Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market Size, Share and Forecast, By Application, 2020-20269.2. Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market Size, Share and Forecast, By Application, 2027-20339.3. Electricity9.4. Heat
10.1. Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market Size and Market Share
11.1. Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market Size and Market Share By Region (2020-2026)11.2. Vietnam Waste to Energy (WtE) Market Size and Market Share By Region (2027-2033)11.3. Eastern Region11.4. Western Region11.5. Northern Region11.6. Southern Region
12.1. Becamex IDC Corp.12.1.1. Company details12.1.2. Financial outlook12.1.3. Product summary12.1.4. Recent developments12.2. C&G Environmental Protection Holdings Ltd12.2.1. Company details12.2.2. Financial outlook12.2.3. Product summary12.2.4. Recent developments12.3. Hau Giang Biomass Power Joint Stock Company12.3.1. Company details12.3.2. Financial outlook12.3.3. Product summary12.3.4. Recent developments12.4. Hitachi Zosen Corporation12.4.1. Company details12.4.2. Financial outlook12.4.3. Product summary12.4.4. Recent developments12.5. T&J Green Energy12.5.1. Company details12.5.2. Financial outlook12.5.3. Product summary12.5.4. Recent developments12.6. Tam Sinh Nghia Investment and Development JSC12.6.1. Company details12.6.2. Financial outlook12.6.3. Product summary12.6.4. Recent developments12.7. Thuan Thanh Environment Joint Stock Company (TT)12.7.1. Company details12.7.2. Financial outlook12.7.3. Product summary12.7.4. Recent developments12.8. Vietnam Waste Solutions (VWS)12.8.1. Company details12.8.2. Financial outlook12.8.3. Product summary12.8.4. Recent developments12.9. Vietstar Joint Stock Company12.9.1. Company details12.9.2. Financial outlook12.9.3. Product summary12.9.4. Recent developments12.10. Watrec Ltd12.10.1. Company details12.10.2. Financial outlook12.10.3. Product summary12.10.4. Recent developments12.11. Others
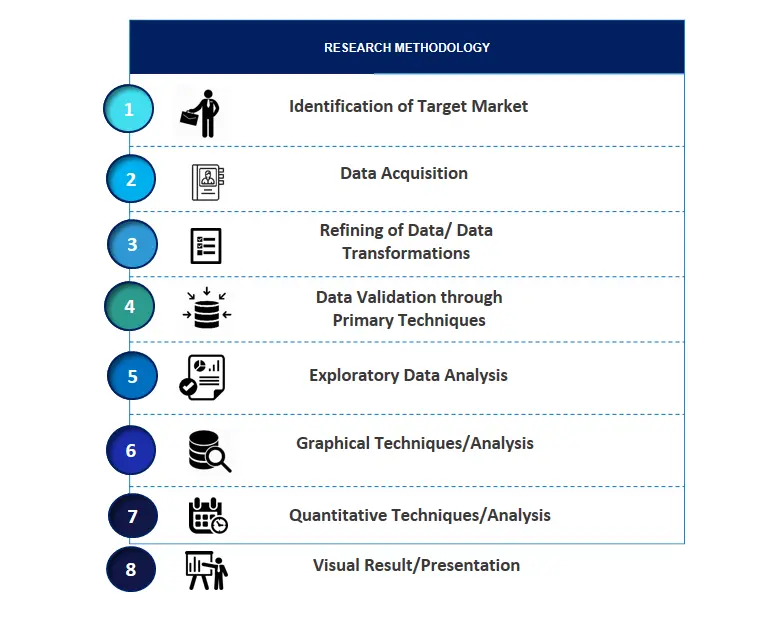
SPER Market Research’s methodology uses great emphasis on primary research to ensure that the market intelligence insights are up to date, reliable and accurate. Primary interviews are done with players involved in each phase of a supply chain to analyze the market forecasting. The secondary research method is used to help you fully understand how the future markets and the spending patterns look likes.
The report is based on in-depth qualitative and quantitative analysis of the Product Market. The quantitative analysis involves the application of various projection and sampling techniques. The qualitative analysis involves primary interviews, surveys, and vendor briefings. The data gathered as a result of these processes are validated through experts opinion. Our research methodology entails an ideal mixture of primary and secondary initiatives.
Frequently Asked Questions About This Report
PLACE AN ORDER
Year End Discount
Sample Report
Pre-Purchase Inquiry
NEED CUSTOMIZATION?
Request CustomizationCALL OR EMAIL US
100% Secure Payment






Related Reports
Our Global Clients
Our data-driven insights have influenced the strategy of 200+ reputed companies across the globe.