Japan Construction Market Growth, Size, Trends, Share, Revenue, Challenges and Future Outlook
Japan Construction Market Size- By Sector- Regional Outlook, Competitive Strategies and Segment Forecast to 2033
| Published: May-2023 | Report ID: COAM2314 | Pages: 1 - 106 | Formats*: |
| Category : Construction & Manufacturing | |||
-00654264052023.jpg)
-00655304052023.jpg)
| Report Metric | Details |
| Market size available for years | 2019-2033 |
| Base year considered | 2022 |
| Forecast period | 2023-2033 |
| Segments covered | By Sector |
| Regions covered | Chubu, Chugoku, Hokkaido, Kansai, Kanto, Kyushu, Shikoku, Tohoku |
| Companies Covered | Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd, Nippon Concrete Industries, Obayashi Corp., Takada Corporation, The Zenitaka Corp |
- Academic and Researchers
- Construction Companies and Contractors
- Government Agencies
- Industry Associations and Trade Organizations
- Investors
- Suppliers and Manufacturers
- Japan Construction Market Value Share and Forecast, By Sector, 2023-2033
- Commercial
- Energy and Utilities
- Industrial
- Infrastructure
- Residential
- Chubu
- Chugoku
- Hokkaido
- Kansai
- Kanto
- Kyushu
- Shikoku
- Tohoku
- Japan Construction Market Size (FY’2023-FY’2033)
- Overview of Japan Construction Market
- Segmentation of Japan Construction Market By Sector (Commercial, Energy and Utilities, Industrial, Infrastructure, Residential)
- Statistical Snap of Japan Construction Market
- Growth Analysis of Japan Construction Market
- Problems and Challenges in Japan Construction Market
- Competitive Landscape in the Japan Construction Market
- Impact of COVID-19 and Demonetization on Japan Construction Market
- Details on Recent Investment in Japan Construction Market
- Competitive Analysis of Japan Construction Market
- Key Players in the Japan Construction Market
- SWOT Analysis of Japan Construction Market
- Japan Construction Market Future Outlook and Projections (FY’2023-FY’2033)
- Recommendations from Analyst
1.1. Scope of the report1.2. Market segment analysis
2.1. Research data source
2.1.1. Secondary Data2.1.2. Primary Data2.1.3. SPER’s internal database2.1.4. Premium insight from KOL’s
2.2. Market size estimation
2.2.1. Top-down and Bottom-up approach
2.3. Data triangulation
4.1. Driver, Restraint, Opportunity and Challenges analysis
4.1.1. Drivers4.1.2. Restraints4.1.3. Opportunities4.1.4. Challenges
4.2. COVID-19 Impacts of the Japan Construction Market
5.1. SWOT Analysis
5.1.1. Strengths5.1.2. Weaknesses5.1.3. Opportunities5.1.4. Threats
5.2. PESTEL Analysis
5.2.1. Political Landscape5.2.2. Economic Landscape5.2.3. Social Landscape5.2.4. Technological Landscape5.2.5. Environmental Landscape5.2.6. Legal Landscape
5.3. PORTER’s Five Forces
5.3.1. Bargaining power of suppliers5.3.2. Bargaining power of buyers5.3.3. Threat of Substitute5.3.4. Threat of new entrant5.3.5. Competitive rivalry
5.4. Heat Map Analysis
6.1. Japan Construction Market Manufacturing Base Distribution, Sales Area, Product Type6.2. Mergers & Acquisitions, Partnerships, Product Launch, and Collaboration in Japan Construction Market
7.1. Japan Construction Market Value Share and Forecast, By Sector, 2023-20337.2. Commercial7.3. Energy and Utilities7.4. Industrial7.5. Infrastructure7.6. Residential
8.1. Japan Construction Market Size and Market Share
9.1. Japan Construction Market Size and Market Share by Sector (2019-2026)9.2. Japan Construction Market Size and Market Share by Sector (2027-2033)
10.1. Japan Construction Market Size and Market Share by Region (2019-2026)10.2. Japan Construction Market Size and Market Share by Region (2027-2033)10.3. Chubu10.4. Chugoku10.5. Hokkaido10.6. Kansai10.7. Kanto10.8. Kyushu10.9. Shikoku10.10. Tohoku
11.1. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd
11.1.1. Company details11.1.2. Financial outlook11.1.3. Product summary11.1.4. Recent developments
11.2. Nippon Concrete Industries
11.2.1. Company details11.2.2. Financial outlook11.2.3. Product summary11.2.4. Recent developments
11.3. Obayashi Corp.
11.3.1. Company details11.3.2. Financial outlook11.3.3. Product summary11.3.4. Recent developments
11.4. Takada Corporation
11.4.1. Company details11.4.2. Financial outlook11.4.3. Product summary11.4.4. Recent developments
11.5. The Zenitaka Corp.
11.5.1. Company details11.5.2. Financial outlook11.5.3. Product summary11.5.4. Recent developments
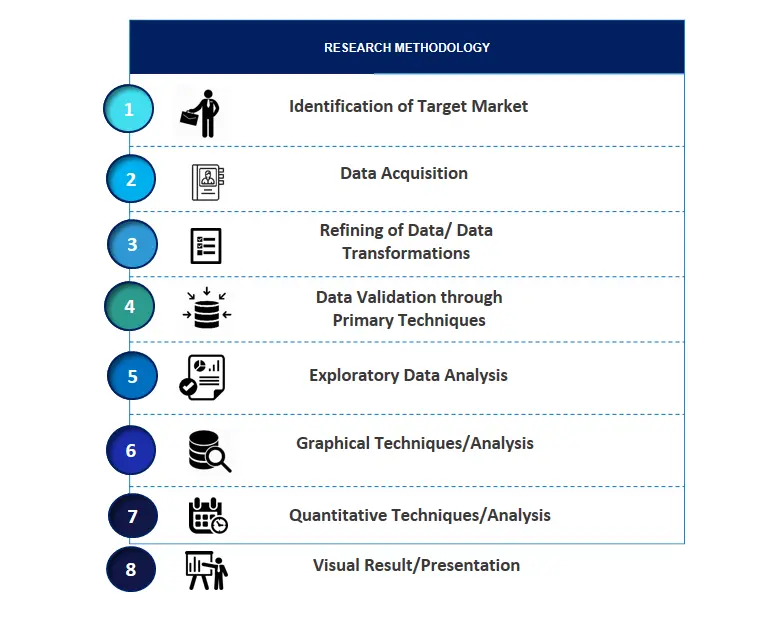
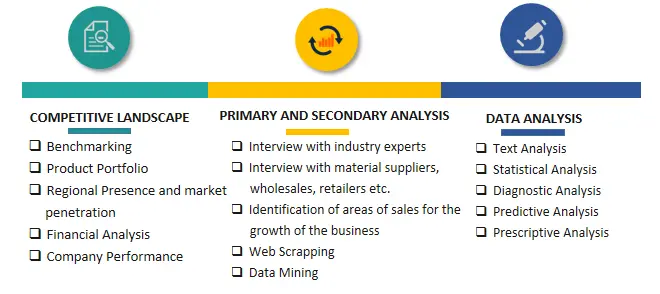
SPER Market Research’s methodology uses great emphasis on primary research to ensure that the market intelligence insights are up to date, reliable and accurate. Primary interviews are done with players involved in each phase of a supply chain to analyze the market forecasting. The secondary research method is used to help you fully understand how the future markets and the spending patterns look likes.
The report is based on in-depth qualitative and quantitative analysis of the Product Market. The quantitative analysis involves the application of various projection and sampling techniques. The qualitative analysis involves primary interviews, surveys, and vendor briefings. The data gathered as a result of these processes are validated through experts opinion. Our research methodology entails an ideal mixture of primary and secondary initiatives.
Frequently Asked Questions About This Report
PLACE AN ORDER
Year End Discount
Sample Report
Pre-Purchase Inquiry
NEED CUSTOMIZATION?
Request CustomizationCALL OR EMAIL US
100% Secure Payment






Related Reports
Our Global Clients
Our data-driven insights have influenced the strategy of 200+ reputed companies across the globe.